Technology
Our regenerative biological products can be used for a variety of chronic wounds, using proven technology to bring relief to patients in need.



Skin Grafts
Biologicals used to treat chronic wounds resistant to standard or traditional forms of treatment.
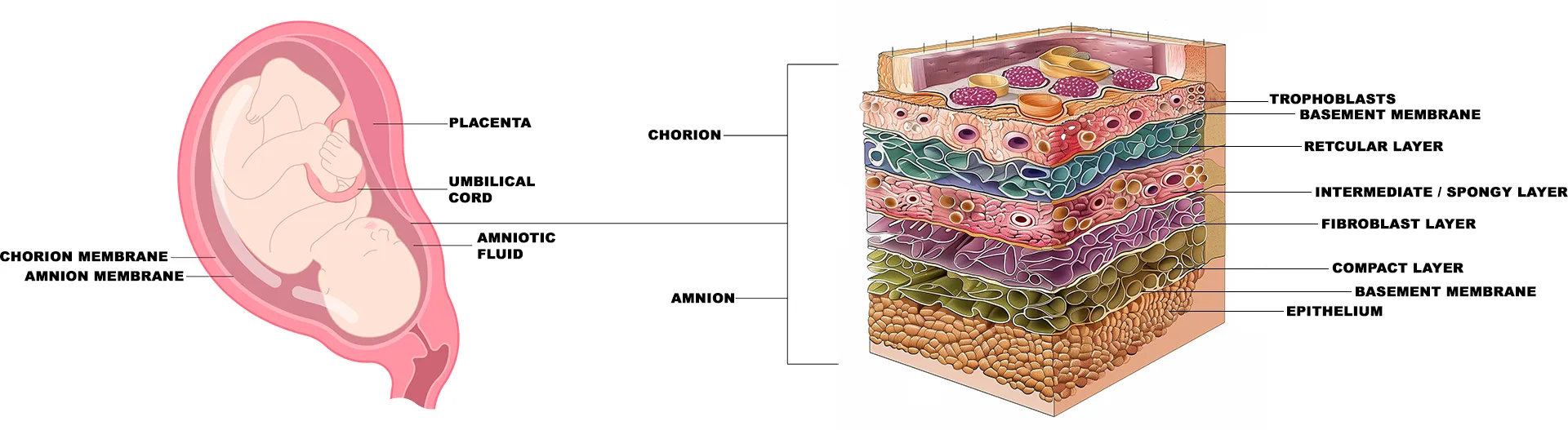
Amniotic Membrane
The amniotic membrane represents the innermost layer of the placenta and is composed of a single epithelial layer, a thick basement membrane and an avascular stroma. The special structure and biological viability of the amniotic membrane allows it to be an ideal candidate for creating scaffolds used in tissue engineering. Epithelial cells derived from the amniotic membrane have the advantages of stem cells, yet are a more suitable source of cells for tissue engineering than stem cells.
Skin Grafts can be derived from:
Chorion – The outer membrane surrounding an embryo that contributes to the formation of the placenta, and acts as a protective barrier during development.
Amnion – The innermost membrane that encloses the embryo and filled with amniotic fluid, which holds the embryo in suspension.
* Human tissues are obtained by consenting C-section donors.
Skin Grafts
Biologicals used to treat chronic wounds resistant to standard or traditional forms of treatment.
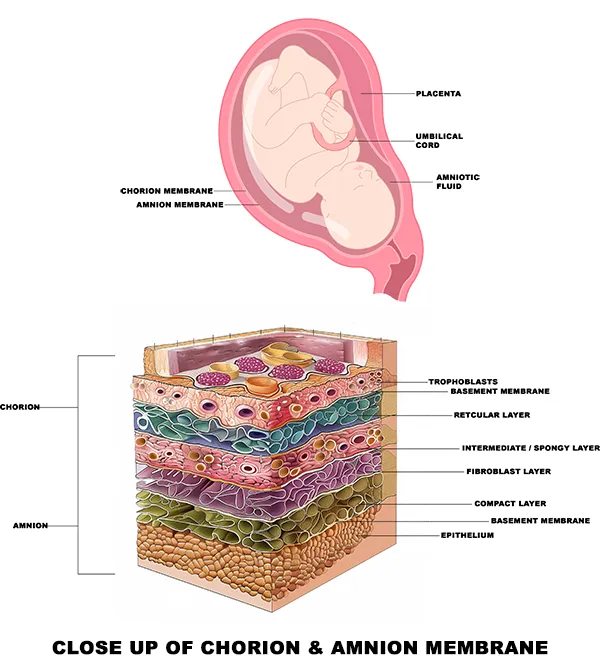
Amniotic Membrane
The amniotic membrane represents the innermost layer of the placenta and is composed of a single epithelial layer, a thick basement membrane and an avascular stroma. The special structure and biological viability of the amniotic membrane allows it to be an ideal candidate for creating scaffolds used in tissue engineering. Epithelial cells derived from the amniotic membrane have the advantages of stem cells, yet are a more suitable source of cells for tissue engineering than stem cells.
Skin Grafts can be derived from:
Chorion – The outer membrane surrounding an embryo that contributes to the formation of the placenta, and acts as a protective barrier during development.
Amnion – The innermost membrane that encloses the embryo and filled with amniotic fluid, which holds the embryo in suspension.
* Human tissues are obtained by consenting C-section donors.
Tissue Sourcing & Application
Grafts may be used to treat many types of “non-healing” wounds, such as venous ulcers, pressure ulcers, diabetic ulcers, arterial ulcers, and any other wound with exposed vital structures.
Ulcer Types
Venous Ulcers
A venous ulcer (venous stasis ulcer), occurs on the skin and takes an extended time to heal, usually because of venous insufficiency–a condition where the flow of blood through the veins is inadequate, causing blood to pool in the legs.
This condition is often chronic and results from malfunctioning valves in the veins of the legs, which leads to increased pressure in the veins, fluid build-up, and eventually, skin breakdown and ulceration.
Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bedsores, or decubitus ulcers, are injuries to the skin and underlying tissue resulting from prolonged pressure on the skin. They often develop on skin that covers bony areas of the body, such as the heels, ankles, hips, and tailbone.
People most at risk of pressure ulcers are those with a medical condition that limits their ability to change positions or those who spend most of their time in a bed or chair.
Diabetic Ulcers
Diabetic ulcers are open sores or wounds that occur in individuals with diabetes, most commonly on the foot. They are a significant complication of diabetes, particularly in those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, neuropathy (nerve damage), and peripheral arterial disease (PAD). These ulcers are a leading cause of foot amputations among people with diabetes due to their potential for infection and poor healing.
Arterial Ulcers
Arterial ulcers, also known as ischemic ulcers, are wounds that develop due to inadequate blood flow, typically in the arteries, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. This condition is often a consequence of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), where the arteries that carry blood to your limbs become narrowed or blocked. Arterial ulcers are most commonly found on the feet and legs.
Stages of Wound
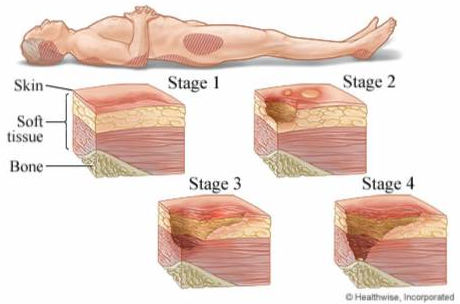
STAGE 1
Erythema of the skin only
STAGE 2
Erythema with the loss of partial thickness of the skin including epidermis and part of the superficial dermis
STAGE 3
Full thickness ulcer that might involve the subcutaneous fat
STAGE 4
Full thickness ulcer with the involvement of the muscle or bone
